Impact of Plant Essential Oils On The Nervous System
This article focuses on the nervous system and provides an overview of the potential impact of plant essential oils on various functions regulated by the central nervous system, including stress, anxiety, and cognitive functions.
Overview
Studies have explored how essential oils may benefit emotional, mood, and cognitive functions to broaden understanding and expand perspectives on natural therapeutic interventions for personal management.
One important aspect of natural oils is that plant essential oils are not known to create a physical or psychological dependence. They are also generally regarded as safe “GRAS.”
This article extensively references the recent study by Sattayakhom et al. (2023).
1. Classical Sciences, Healing Oils & Neural System
In the same way, traditional science recognises several uses for the therapeutic actions of certain plant essential oils that impact the nervous system.
For example, lavender and rosemary oils may improve mental and emotional well-being due to their anti-stress, anti-anxiety, sedative, and other beneficial effects.
2. Application Methods (Method Of Use)
Plant oils are used to support the well-being of the nervous system through various methods, including inhalation, topical application, and ingestion, as suggested by studies and traditional disciplines.
Body Response To Inhalation Via Olfactory System
From the above methods or routes of application-use, according to (Sattayakhom et al., 2023), inhaling essential oils through the olfactory system is the fastest and easiest method.
Inhalation has been the most popular route of administration at approximately 58.57% according to their data.
Secondly, plant oil may immediately change the autonomic nervous system and physiological responses, including pupil dilation, blood pressure, muscle tone, pulse rate, skin temperature, and brain activity.
Observed State Change: “15 Minute Period”
The authors further state that bodily responses can improve physical, mental, and emotional well-being after just 15 minutes of inhalation.
Furthermore, the authors also report the key systems that are influential in the effectiveness of plant oils, primarily or the starting point being the olfactory receptors.
Role of Olfactory Receptors
Subsequently, their study suggests that the olfactory receptors in the nasal olfactory epithelium (thin tissue lining) detect essential oils (EOs) components.
This stimulation activates olfactory nerves and transmits a signal to the central nervous system, including the limbic system and hypothalamus, further modulating human behaviour and body function.
And it further indicates that the nervous system is the first mechanism of the body’s response to EOs.

India Ayurveda
Subsequently, some plant oils have a long-standing application history in sciences, such as in Ayurveda, which involves the five elements: earth, water, fire, air, and ether—several oils, such as chamomile and lemongrass are recognised in this.
Latin Quinta Essentia
In the same way, according to (Sattayakhom et al., 2023), “essential oil” comes from “quinta essentia” in ancient Latin, which means the fifth element. The fifth element is the spirit or life force integrated with the other four elements: fire, air, earth, and water.
This categorisation is similar to the Ayurvedic categorisation of “Prana”, which is vital energy, life force or spirit.
Furthermore, (Sattayakhom et al., 2023) state that the isolation of essential oil was believed to separate the spirit from the plant.
The oils were used as healing essences with medical benefits.
A Brief Overview Of The Nervous System Functions
Subsequently, when taking into account the nervous system and its functions; it coordinates movement, regulates body functions, processes sensory information, and controls behaviour and emotions.
- The nervous system includes the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, a crucial part of the central nervous system (CNS).
- The CNS processes and transmits information throughout the body, controls movement, regulates bodily functions, and influences behaviour and emotions.
- This network plays a crucial role in overall well-being, it can be influenced by various factors and plant essential oils are one influential factor.

Therapeutic Effects & State Changes Induced (Depending On Oil Type)
- Cognitive functions, memory, alertness
- Reduce mental fatigue
- Improve mood
- Regulatory effects on emotional behaviour
- Anxiolytic anti anxiety
- Helpful in depression
- Anti stress
- Reduce negative emotions
- Alleviate fatigue, multidimensional fatigue
- Pain management
- Positive distraction
- Reduce agitated behaviour
- Improve sleep
- Reduce cravings
- Calming, uplifting, relaxing, sense of well-being, refreshing etc
- Reduce perception of mental burnout
- Reduce disruptive behaviour
- Several other influences
A Basic Allrounder Plant Essential Oil
Overall and as an allrounder, amongst the thousands of plants and plant oils available, lavender essential oil (Lavandula Angustifolia) has been studied extensively and recognised as helpful in several of the above areas.
However, there are numerous other oils that may be more helpful depending on individual health status and suitability.
3. Understanding Plant Essential Oils (EO)
Essential oils are natural compounds extracted from plants, known for their aromatic properties and therapeutic benefits.
These highly concentrated oils capture the plant’s aroma and flavour. They are commonly used in aromatherapy, skin care, and holistic medicine.
Each essential oil has unique properties and potential therapeutic effects. Also, depending on the plant type method of oil extraction varies.
Factors That Influence Effectiveness Of EOs
- The efficacy of a plant essential oil can be influenced by various factors such as the plant species, growing conditions, extraction method, and storage.
- Specific chemical composition of the oil, including the presence of bioactive compounds, also plays a crucial role in determining its effectiveness.
- Additionally, the purity and quality of the essential oil, as well as its proper dilution and application, can impact its overall efficacy.
General Precautions
Due to their potency, diluting essential oils before applying them to the skin and using them cautiously is important. A balanced approach is vital to any therapeutic resource.
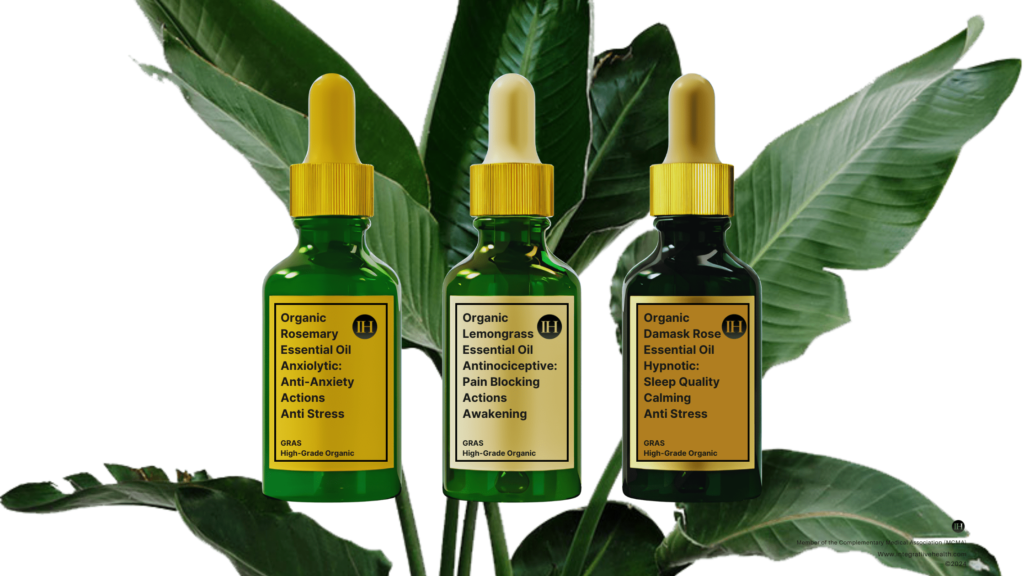

Bioactive Compounds “Terpenes” In Plant Essential Oils
In addition to aromatic compounds, essential oils also contain terpenes (terpenoids are derived from terpenes), which are the main compounds responsible for the unique scents and flavours found in plants.
(Sattayakhom et al., 2023) State, that they are the main components (comprising approximately 80%), but phenylpropanoid provides the flavour and odour of the EOs.
An example of a terpene would be limonene from lemongrass and a terpenoid-geraniol from rose.
Commonly Used Plant Oils According To Data
According to the PubMed database referenced by (Sattayakhom et al., 2023), 81.43% of the plant essential oils studies have been conducted on humans.
- Lavender essential oil was the most commonly used, appearing in approximately 30.71% of the studies.
- The second most popular category of essential oil in the studies is the Citrus spp., which includes essential oils such as orange, bergamot, grapefruit, and lemon (24.4%).
- Rosemary essential oil was the third most used after lavender oil and Citrus spp. oil (5.51%). Mint, rose, cedar wood, geranium, lemon grass, chamomile, cinnamon, and others were also used in smaller amounts.
Further Takeaways From (Sattayakhom et al., 2023)
- Essential oils have therapeutic properties due to their several bioactive compounds.
- The dominant compounds are terpenoids, as well as others.
- Therapeutic actions include anti-stress, anti-anxiety, analgesic, cognitive, and autonomic effects.
- Inhalation is a fast and effective method to use certain plant essential oils.
- The application of these essential oils can also alter levels of neurotransmitter receptors, which can significantly impact mood, behaviour, and brain function.
5. A List Of Helpful Plant Essential Oils For Neural Well-being
Rosmarinus Officinalis: Rosemary OIl.
Damascena Rosa: Damask Rose
Cymbopogon Citratus: Lemongrass
Lavandula: Lavender
Jasmine: Jasminum Officinale
Eucalyptus: Eucalyptus Globulus
Geranium: Pelargonium Graveolens
Chamomile: Matricaria chamomilla
Clary sage: Salvia sclarea
Thyme: Thymus vulgaris
Peppermint: Mentha piperita
Damascena Rosa: Damask Rose
Summary
In summary, plant essential oils range in the thousands due to the several types of species.
With the growing need for better, natural and accessible self care agents, plant essential oils are becoming more popular than before.
However essential oils maintain a long standing history of therapeutic use in traditional disciplines such as Ayurveda. The use of any therapeutic dose is subject to a safety method.
Essential oils interact with the olfactory receptors, influencing the nervous system and other related areas. They are known to induce anti-stress, anti-anxiety, cognitive, emotional, and mood regulation.
These oils are derived from plants, data suggests that bodily responses to inhalation of certain oils can improve physical, mental, and emotional well-being after just 15 minutes of inhalation.
Inhalation has been the most popular route of administration at approximately 58.57%.
Essential oils are generally considered safe (GRAS), suitability of any essential oil depends entirely on individual health status.
Precautions & Suitability
Precautions and personal responsibility are crucial. Before starting any therapeutic agent or routine, it is important to check its suitability for individuals with chronic health concerns or pregnant women.
Seek the advice of a professional. This is an informational post only and does not constitute professional advice.
References in this article
Sattayakhom A, Wichit S, Koomhin P. The Effects of Essential Oils on the Nervous System: A Scoping Review. Molecules. 2023 Apr 27;28(9):3771. doi: 10.3390/molecules28093771. PMID: 37175176; PMCID: PMC10180368.
Yoo KY, Park SY. Terpenoids as potential anti-Alzheimer’s disease therapeutics. Molecules. 2012 Mar 19;17(3):3524-38. doi: 10.3390/molecules17033524. PMID: 22430119; PMCID: PMC6268347.
Lai Shi Min S, Liew SY, Chear NJY, Goh BH, Tan WN, Khaw KY. Plant Terpenoids as the Promising Source of Cholinesterase Inhibitors for Anti-AD Therapy. Biology (Basel). 2022 Feb 14;11(2):307. doi: 10.3390/biology11020307. PMID: 35205173; PMCID: PMC8869317.
Nervousness and Nervines. Dent Regist. 1877 May;31(5):218-219. PMID: 33696067; PMCID: PMC6903032.
Dold M, Bartova L, Volz HP, Seifritz E, Möller HJ, Schläfke S, Kasper S. Efficacy of Silexan in patients with anxiety disorders: a meta-analysis of randomized, placebo-controlled trials. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2023 Oct;273(7):1615-1628. doi: 10.1007/s00406-022-01547-w. Epub 2023 Jan 30. PMID: 36717399; PMCID: PMC10465640.