How Rosemary Oil Awakens The Brain & Better Mood?
Rosemary oil has long-standing historical use in therapeutics due to its medicinal properties. Modern science recognises its positive stimulatory effects on brain and mood activity.
For instance, “Brain wave activities, autonomic nervous system responses, and mood states may be modified with rosemary oil inhalation as found by (Sayorwan et al., 2013).”
In recent years, Rosemary oil has been presented as helpful in promoting hair growth, but it also has other important therapeutic uses, such as stimulating cognitive functions.
Understanding Rosemary Oil, Brain & Mood Link
This article aims to explore the following main points related to rosemary oil, which include:
- An overview of rosemary oil bioactive constituents.
- Any relevant case study related to rosemary oil, brain and mood.
- Ayurvedic sciences application of rosemary oil.
- Why rosemary oil may be helpful as an integrated therapeutic for cognitive vitality.
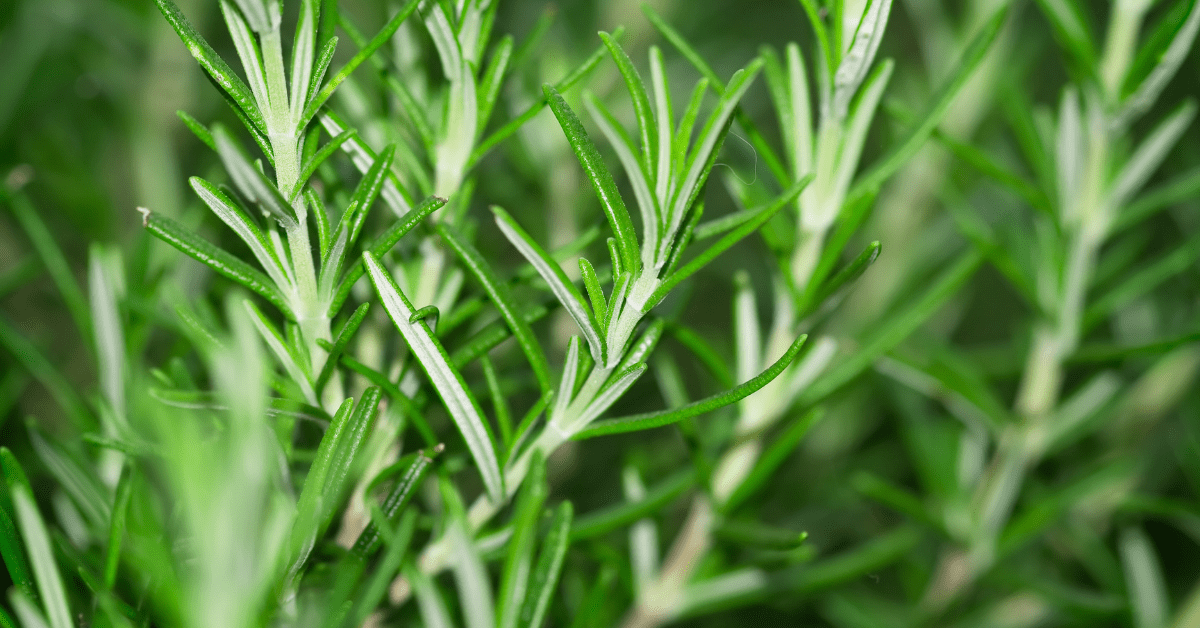
Rosemary Oil
Rosemary, also known as Rosmarinus officinalis, has been extensively used in traditional medicine throughout ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, China and India (Nema et al., 2022).
It is believed to be native to the Mediterranean region but has grown in many other parts of the world.
Today, Rosemary is a well-known kitchen plant used in several cuisines. However, this differs from using it in a therapeutic setting for health and well-being purposes.
Physical Characteristics Of Rosemary
The physical characteristics of the rosemary plant are that it is an evergreen shrub with needle-like leaves.
It has small blue or pink flowers.
Aroma of Rosemary
Rosemary has a strong aroma, and it is deep, herbaceous, woody, and slightly camphorous.

As A Traditional Therapeutic Agent
- Traditional medicine: Rosemary oil has been used for a variety of purposes, including improving memory and concentration, relieving pain and sore muscles, and enhancing hair growth.
- Medicinal properties: Rosemary oil contains bioactive compounds with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties. These compounds have been shown to have various potential health benefits, including reducing inflammation, boosting the immune system, and improving digestion.
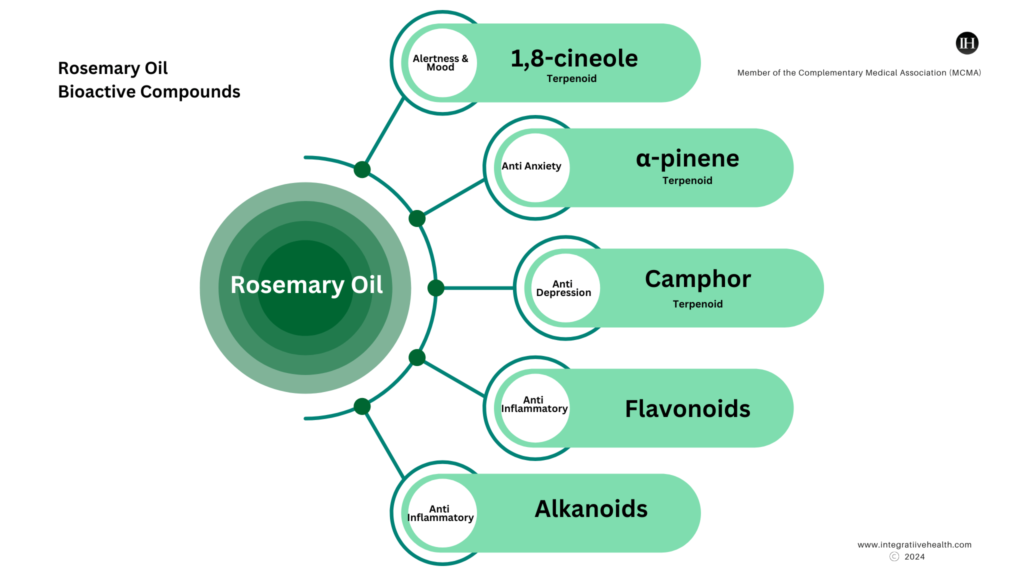
1,8-cineole & Other Phytochemicals In Rosemary Oil
1,8-cineole is a phytochemical in rosemary that has been studied for its effects on the central nervous system.
Research suggests that 1,8-cineole may positively impact brain function and mood.
- In particular, it may improve cognitive performance, such as alertness and memory in healthy individuals, as explored by (Moss & Oliver, 2012) in their study, “Plasma 1,8-cineole correlates with cognitive performance following exposure to rosemary essential oil aroma” (Therapeutic Advances in Psychopharmacology).
- Additionally, others suggest that 1,8-cineole may have mood-enhancing properties, potentially reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression (Sayorwan et al., 2013; Moss et al., 2017). However, optimal dose delivery methods and individual factors play a key role in its potential and effect.
Other vital phytochemicals in the oil are terpenoids, essential oils, alkaloids and flavonoids (Rahbardar & Hosseinzadeh, 2020).
Specifically, 19.41% α-pinene, 20.08% 1,8-cineole, and 21.25% camphor are the key constituents in rosemary (Sayorwan et al., 2013).

Example Case Study: Investigated Effects Of Rosemary Oil Inhalation
In a study by (Sayorwan et al., 2013) which is published in the journal Scientia Pharmaceutica, the effects of inhaled rosemary oil on cognitive function and mood were examined.
Method Applied: They used two methods for inhalation: direct inhalation and inhalation through a diffuser.
Below are some of its key points explored.
Effects On Cognition
The study found that participants who inhaled rosemary oil had improved cognitive performance, including better memory and concentration, compared to those who did not inhale the oil.
Memory
Concentration
Effects On Mood
Subsequently, the oil displayed mood-regulating effects as well, and some of the effects on mood included the following:
- Reduced stress levels and increased contentment after inhaling the oil.
- The study suggests that the cognitive benefits of rosemary oil may be due to its ability to increase levels of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter involved in learning and memory processes.
- The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of rosemary oil may also contribute to its positive effects on cognitive function.
- Rosemary oil inhalation led to changes in the activities of the nervous system as measured by electroencephalography (EEG).
- Overall, the study supports using (RO) as a natural and effective way to help cognitive function and regulate mood.
The authors concluded that essential oil inhalation could be a safe and effective method to improve cognitive function, mood, and sleep.
The complete study can be read on the following link.
Rosemary oil has a pronounced action on the brain and central nervous system (CNS). A powerful tool in helping clear the mind and increasing mental awareness. It has also been shown to possess excellent brain-stimulating properties and aid in memory improvement.
Faixová and Faix (2008)
An Overview of Acetylcholine Neurotransmitter (ACh)
Furthermore, as seen from the previous section, the study conducted by Sayorwan et al. also suggests that the cognitive benefits of rosemary oil may be due to its ability to increase levels of acetylcholine (ACh), a neurotransmitter involved in learning and memory processes.
Below is an overview to help understand its association with cognitive functions:
- Acetylcholine plays a critical role in forming and consolidating memories, and its breakdown has been linked to cognitive impairment and memory loss.
- ACh can regulate the normal cholinergic signal transduction associated with learning and memory (Chen et al., 2022).
- Stimulating effects of acetylcholine by rosemary oil are associated with influencing cognitive function, including memory and concentration.
Rosemary Oil On Brain Wave Activity
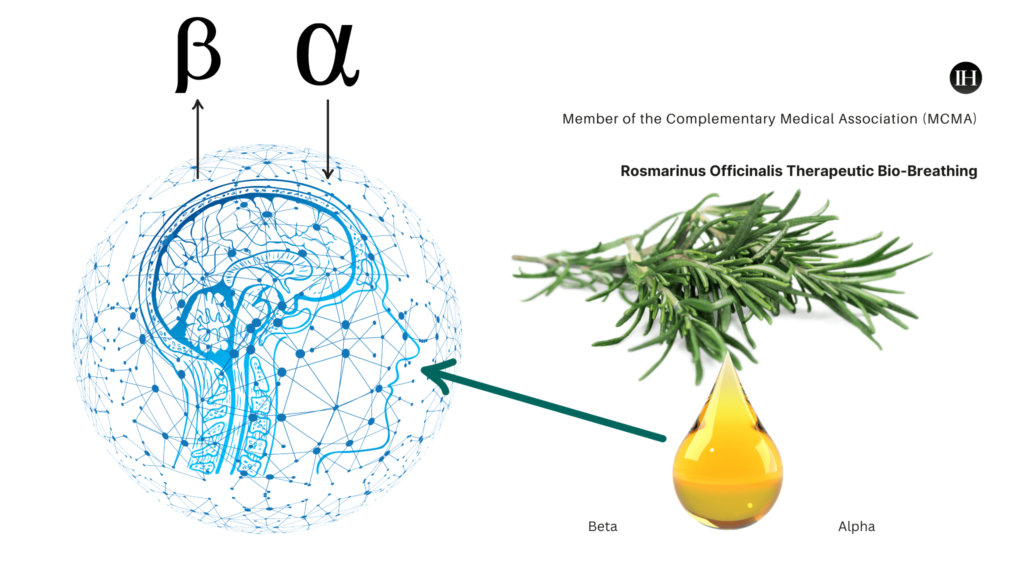
Sayorwan et al. (2013) found that inhalation of rosemary oil significantly affected brain wave activities.
Specifically, it decreased alpha wave activity, which is associated with relaxation, and increased beta wave activity, which is associated with increased alertness and improved cognitive performance.
- The power of alpha1 (8–10.99 Hz) and alpha2 (11–12.99 Hz) waves is reduced on RO inhalation.
- An increase in beta wave power (13-30 Hz) was observed in the anterior brain region on RO inhalation.
Additionally, to help understand brain wave activity and rosemary oil, we explore beta brain waves below in a limited manner.
An Overview of Beta Brain Waves
Beta waves are a type of electrical activity that occur in the brain when we are awake and engaged in mental activities.
- They are associated with good cognitive function because they help us process information quickly and efficiently. Furthermore, they process sensory information and coordinate movement.
- Beta waves also play a role in regulating our mood. They are often found in greater amounts in alert, focused, and motivated individuals.
Location Of Beta
The main location of beta waves in the brain is the frontal cortex, which is responsible for executive functions such as decision-making, planning, and working memory.
However, beta waves can also be found in other brain areas.
Mood State: Post Rosemary Oil Inhalation
Furthermore, in terms of RO’s impact on mood, (Sayorwan et al., 2013) also found that individuals became more “active” and felt “fresher.”
Active
Fresher

Method & Dose In Study
The following section explores the method and dosage used in the study of rosemary oil inhalation.
- Healthy adults participated in the study.
- Before the experiments, individuals rated the pleasantness of the aroma. Individuals were selected based on the rates of pleasantness within 2-4.
- A base oil of sweet almond oil was used.
- Rosemary oil was administered in a concentration of 10% v/v (volume/volume) using an oxygen pump connected to a respiratory mask with a plastic tube (adult inhalation set), with an airflow rate of 2 litres/min.
Other Therapeutic Methods
Rosemary oil is generally considered safe for healthy adults as specified by several reputable sources.
However, it is crucial to assess its suitability and seek professional advice before incorporating it into a routine.
Here are a few examples of other methods of use:
Dry Method Bio-Breathing (Inhalation Exhalation)
- Take a small piece of clean natural cloth.
- Add 2-3 drops of rosemary oil to the centre of the cloth.
- In a comfortable environment, hold the cloth a few inches away from your nose and breathe normally.
- Exhale slowly and repeat the process for 2-3 minutes.
- Exercise caution not to hold the cloth close to your face to avoid irritation.
Wet Method Bio-Breathing (Inhalation Exhalation)
- Wet or dry inhalation is a different method of use.
- For instance, a cloth dipped in a mixture of clean water (warm or cold) with a few drops of rosemary oil, dipping and then squeezing the cloth before use, or
- A in a warm bath and or steam.
Anti-inflammatory & Anti-Oxidative
Additionally, rosemary oil’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties may contribute to its positive effects on cognitive function. Inflammation and oxidative stress are believed to be factors that can affect cognitive decline.
As a result reducing these factors may help to protect against cognitive impairment.
Therefore, rosemary oil may be an effective and natural way to support cognitive function and protect against these stressors.
Ayurvedic Categorisation: Rosemary Oil, Vata & Kapha Pacifying
In Ayurvedic sciences, rosemary oil contains thermogenic properties; therefore, it is a Pitta-enhancing plant. One of the key compounds is called camphor, which has a warming effect on the body and can help to increase circulation.
As a result, it is prescribed to help balance the vata and kapha doshas.
For instance, it can have a calming effect on the nervous system, which helps balance the excess vata dosha. Additionally, its warming properties help stimulate circulation and promote relaxation, making it an ideal remedy for vata imbalance.
Here are some points on its thermogenic properties:
- Ayurveda suggests rosemary’s warming nature helps to improve digestion and metabolism, while also promoting healthy blood circulation.
- Rosemary can help balance the Vata and Kapha doshas, as it helps calm the nervous system reduce stress, anxiety and improve mental clarity. This application in Ayurveda co-relates with the former studies referenced in this article.

Summary & Key Takeaways
In summary, rosemary oil is a well-known therapeutic with a long-standing history of use in ancient cultures and traditional sciences.
Many scientific studies now recognize its stimulating effects on cognitive function, as discussed in this article.
- It has been found that it can enhance mental activity, including alertness and concentration, as well as improve memory and mood.
- Reducing inflammation and oxidative stress can help protect against cognitive decline linked to these factors.
- Ayurvedic sciences categorise the oil as Vata and Kapha balancing, which helps a sense of mental vitality.
Therefore, integrating rosemary oil into a personalised routine may be a supportive factor for cognitive vitality, depending on individual health status and suitability.
Precautions & Suitability
Precautions and personal responsibility are crucial. Before starting any therapeutic or wellness routine, it is important to check its suitability for individuals with chronic health concerns or pregnant women. The use of rosemary oil may not be appropriate for certain individuals and depends on their health status.
Seek the advice of a professional. This is an informational post only and does not constitute professional advice.
Frequently Asked Questions
Many reputable sources suggest that rosemary oil is generally safe for use, but it’s best to seek professional advice to determine its suitability for your specific needs.
For purity of the extracted oil, organic certifications, to some extent, guarantee free from chemicals. This may also affect the end product efficiency. Therefore, a natural organic source can be a better choice.
It can be tested by adding 1-2 drops of organic essential oil onto a clean cloth and breathing its aroma at a distance (according to suitability & precautions).
References & online source(s) in this article:
- Sayorwan, W., Ruangrungsi, N., Piriyapunyporn, T., Hongratanaworakit, T., Kotchabhakdi, N., & Siripornpanich, V. (2013). Effects of Inhaled Rosemary Oil on Subjective Feelings and Activities of the Nervous System. Scientia Pharmaceutica, 81(2), 531-542. https://doi.org/10.3797/scipharm.1209-05
- Rahbardar, M. G., & Hosseinzadeh, H. (2020). Therapeutic effects of rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) and its active constituents on nervous system disorders. Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences, 23(9), 1100-1112. https://doi.org/10.22038/ijbms.2020.45269.10541
- Moss M, Cook J, Wesnes K, Duckett P. Aromas of rosemary and lavender essential oils differentially affect cognition and mood in healthy adults. Int J Neurosci. 2003 Jan;113(1):15-38. doi: 10.1080/00207450390161903. PMID: 12690999.
- Haam, J., & Yakel, J. L. (2017). Cholinergic modulation of the hippocampal region and memory function. Journal of Neurochemistry, 142(Suppl 2), 111. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.14052
- Chen, R., Huang, B., Yang, L., & Hong, F. (2022). Role of Cholinergic Signaling in Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules, 27(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27061816
- Faixová, Zita & Faix, S.. (2008). Biological effects of rosemary essential oil (Review). Folia Veterinaria. 52. 135-139.
- Moss, M., & Oliver, L. (2012). Plasma 1,8-cineole correlates with cognitive performance following exposure to rosemary essential oil aroma. Therapeutic Advances in Psychopharmacology, 2(3), 103-113. https://doi.org/10.1177/2045125312436573
- MCMA, MA Hunjan, G. G. (2024) InteGratiiveHealth.com
Apart from Rosemary oil, there are a number of other EOs that offer different therapeutic values for helping soothe stress and anxiety, improve moods and provide a sense of cognitive vitality. Read more on anxiolytic oils.
Anxiolytic
OILS