Are Sunflower Seeds Good For You? High Value BioDiet
“Are sunflower seeds good for you? Sunflower seeds are rich in a variety of bioactive compounds, including phenolic acids, flavonoids, and lignans. Of particular note, they are a good source of chlorogenic acids, which exhibit antioxidant properties and may contribute to weight loss.
These compounds are recognized for their exceptional antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Remarkably, as a natural phenomenon, the sunflower is known to rotate its head east to follow the direction of the sun.
Key Points In This Article
This article explores sunflower seed bioactive constituents, their therapeutic impact and an overview of Ayurvedic use in a bioactive diet.
Overview: Are Sunflower Seeds Good For You
Sunflower seeds are an excellent source of rich nutrients and therapeutic value, while also being versatile to use. Therefore, they make a positive contribution as part of a well-balanced diet.
According to (Guo et al., 2017), the seeds boast high nutritional value due to their rich content of essential elements such as calcium, selenium, magnesium, folic acid, choline, vitamin A, vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol), and various other components.
This unique combination of constituents and compounds is associated with therapeutic effects on the human body when consumed as part of a well-balanced diet.
An excellent example is Isoflavone, which acts as a phytoestrogen and has been scientifically proven to offer several dietary benefits, including potent antioxidant effects.

The Sunflower Seed “Helianthus Annuus”
The botanical name of this sunflower seed is Helianthus Annuus, and it is a part of the Asteraceae family of plants, also known as the daisy family.
There are several sunflower seeds, including the common sunflower, the giant sunflower, and the dwarf sunflower. The flowers are beautiful and have vibrant hues of golden yellow-orange.
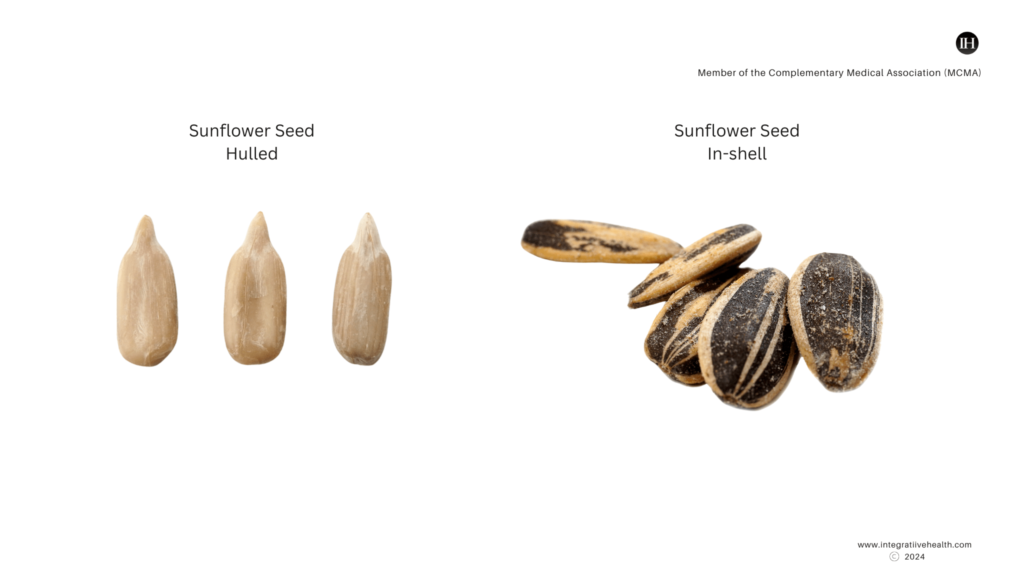
Additionally, there are two types of sunflower seeds: oil-producing and confectionery.
The former has a black seed with a thin hull, while the latter is used for dietary food purposes such as eating the seed as opposed to using it as oil.
| Common Sunflower | Giant Sunflower | Dwarf Sunflower |
Physical & Taste Characteristics
The common sunflower can grow up to 16 feet tall, while the giant sunflower can reach up to 30 feet in height and produce heads over 2 feet in diameter.
Secondly, the dwarf sunflower, on the other hand, grows to a height of only 1 to 2 feet and produces smaller heads.
Here are some key points of its physical characteristics:
- The sunflower petals are typically yellow or orange, with a dark centre. The petals are smooth, while the leaves are rough and hairy.
- Sunflower seeds are small and flat, with a hard outer shell. The seeds are often greyish or black but can be striped or whitish. Seed characteristics may vary based on flower type.
- The texture of sunflower seeds is generally crunchy with a slightly nutty flavour but can vary based on preparation.
- They have many uses, including salads, soups, stews, oils, and snacking.
Origin & Regions
Sunflower seeds are believed to have originated in the Americas, particularly in Mexico and Peru.
Today, they are produced in many countries worldwide, including the United States, Russia, China, Argentina, Turkey, India, and Romania.
The common sunflower is the most widely cultivated and is used for both oil production and dietary consumption.
Common Sunflower A Good Source Of Healthy Fats
The common sunflower, is the most readily available edible variety of sunflower because it is easy to grow and has a high yield.
In terms of nutrient density, the common sunflower is comparable to other sunflower types.
However, the seeds of the common sunflower are larger and have a higher oil content, which makes them a good source of healthy fats.
They are also rich in protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals such as magnesium and selenium. The nutrient content may vary depending on the soil conditions, climate, and other factors, but overall, the common sunflower is a nutritious and versatile food source.
The origin of the name derived from the aspect of the plant which resembled a sun and the fact that it rotates after the sun’s rays
(Petraru et al., 2021)
Nutritional Profile Of Mature & Sun-Dried Sunflower Seeds
The nutritional characteristics of mature and sun-dried sunflower seeds, hulls and kernels contain 33.85% proteins, 65.42% lipids and 2.73% ash, most of which are found in the kernels (Petraru et al., 2021).
In addition, 100 gram of dried seed kernels, according to the United States Department of Agriculture contain the following values;
| Energy 2440 kJ | Protein 20.8 g | Total lipid (fat) 51.5 g | Calcium 78 mg | Iron 5.25 mg |
| Magnesium 325 mg | Phosphorous 660 mg | Potassium 645 mg | Selenium 53 ug | Folate 227 ug |
| Choline 55.1 mg | Betaine 35. 4 mg | Beta Carotene 30 ug | Vitamin A 50 IU | Vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol) 35.2 mg |
Glycemic Index Of Sunflower Seeds
Sunflower seeds have a glycemic index of 35 (Glycemic Index-net), which makes them a great addition to a well-balanced low-GI diet.
This is especially helpful for those looking for high-value nutritional profiles and seeking to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
In addition to high oleic acid and linoleic acid content, the sunflower seed also contains significantly higher amounts of vitamin E (37.8 mg/100 g), compared to linseed, sesame seed, and soy (all of which contain less than 3 mg/100 g) and even peanut
(Guo et al., 2017)
Bioactive Compounds in Sunflower Seeds
Besides their exceptional nutritional content, the seed has several bioactive compounds, part of their micro nutrient profile.
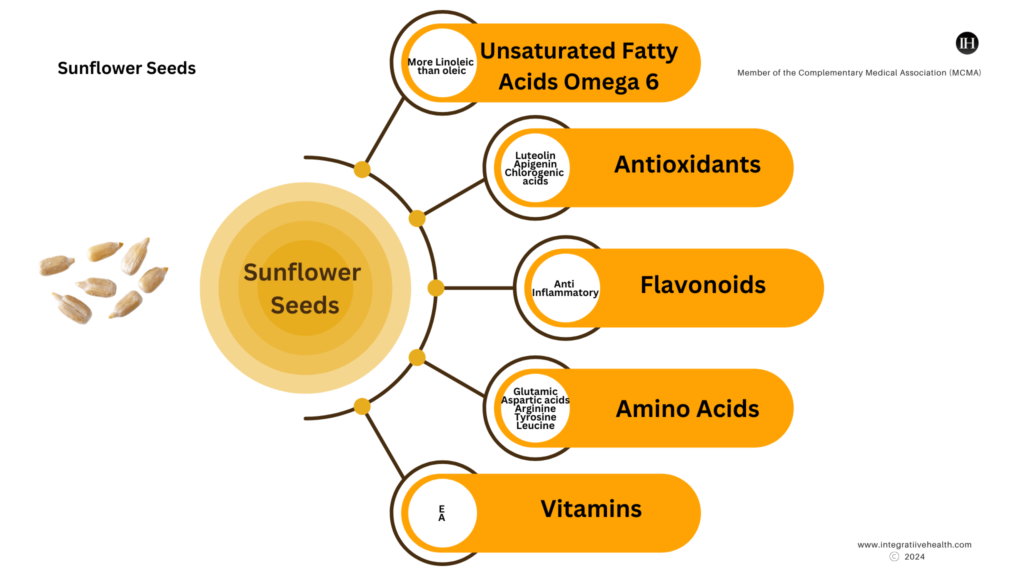
According to (Petraru et al., 2021), the seeds are a source of dietary fibres, unsaturated fatty acids (more linoleic than oleic), antioxidants, flavonoids (quercetin, luteolin, apigenin and kaempferol), amino acids.
Amino Acids
The amino acid profile consists of glutamic and aspartic acids, arginine, phenylalanine, tyrosine, leucine, methionine, and cysteine, which is why they are used in combined complete protein products.
A Good Antioxidant Source
Secondly, Guo et al. (2017) study found that, sunflower seeds and sprouts are rich in antioxidants such as flavonoids, phenolic acids, trace elements, and vitamins.
These antioxidants include heliannone, quercetin, kaempferol, luteolin, and apigenin (flavonoids), as well as caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid, caffeoylquinic acid, gallic acid, protocatechuic, coumaric, ferulic acid, and sinapic acids (phenolic acids).
Subsequently, the compounds have dietary therapeutic and medicinal properties as in vivo & in vitro studies suggest. For instance, some of these include, antioxidative effects, antimicrobial activity, antidiabetic, anti inflammatory etc.
Therapeutic Dietary Actions
Several documented studies establish sunflower seeds’ therapeutic properties, as seen in the previous paragraph.
This is due to the interplay between a rich nutritional profile and high-value bioactive compounds.
Some of these effects result from the particular phytochemicals found in seeds and may be more applicable in the germinated seed.
Here are some terms associated with its dietary therapeutic actions:
Antioxidative
Key compounds:
Phenolic – Isoflavone
Protective against cellular damage
reducing risk of chronic disease
Antimicrobial
Key compounds:
Flavonoids, alkaloids, saponins, and tannins
Antidiabetic
Key compounds:
Phenolic compound, Cynarin. Others, flavonoids, glycosides, and phytosterols
Antihypertensive
Key compounds:
Peptides – ACE inhibitory effects
Anti-inflammatory
Key compounds:
Saponin
The next section explores some of these properties in more detail.
1. Antidiabetic Properties
Sunflower sprouts and seeds have been found to have anti-diabetic properties due to their ability to inhibit advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and their high antioxidant content.
Sunflower sprouts contain cynarin, a phenolic compound that can lower cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
Studies have shown that sunflower seed extract can lower plasma glucose levels and improve various markers of diabetic complications in, (in vivo) observations.
Additionally, sunflower seed extract can effectively control glucose levels by inhibiting alpha-glycosidase, which suppresses intestinal carbohydrate digestion and absorption. (Study link)
2. Antioxidative Properties
In another study by Guo, S., Ge, Y., & Jom, K. N. (2017), it was found that sunflower seedlings contain antioxidants such as enzymes, peptides, carotenoids, and phenolic compounds.
These antioxidants are known to protect against cellular damage and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Some Key Points From The Study:
- The study also revealed that exposure to ultraviolet-B radiation and saline conditions can affect the antioxidant activity of sunflower seedlings.
- Exposure to UV-B radiation and saline conditions can increase the antioxidant defense and enzyme activities in different parts of sunflower plants.
- For example, sunflower cotyledons (the first leaves that appear from a germinating seed.) exposed to UV-B radiation and sunflower seeds exposed to saline exhibit higher activities of antioxidant enzymes.
- Additionally, sunflower leaves in saline conditions show higher activity of certain enzymes compared to the root, while other enzymes show increased activity in the root compared to the leaf under the same conditions.
3. Obesity & Sunflower Seeds Extract
Furthermore, a study conducted by Leverrier et al. (2019), the consumption of Helianthus annuus (sunflower) seed extract for 12 weeks suggests that sunflower seed extract can have an anti-obesity effect on healthy, obese adults.
Per say the results were promising in its anti obesity effect.
The study was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study that showed a significant reduction in body weight and body fat mass in the group that consumed the sunflower seed extract compared to the placebo group.
Based on this, it suggests that Helianthus annuus seed extract may have potential as a natural anti-obesity agent.
Here are some points from the study dose and observations:
Study Dose & Observation
The study involved Sunflower CGA (chlorogenic acid) extract (500 mg/day) for 12 weeks, which contributes to:
- Reducing BMI, waist circumference and body weight, mainly explained by a loss of mass in the fat compartment, more than that in the muscular compartment.
- Those changes may be accompanied by an improved lipid profile, constituting a current approach to preventing cardiovascular diseases and associated obesity diseases, like type 2 diabetes and atherosclerosis.

Sunflower Seed Germination Increases Total Phenolic Content
The process of germination, which fosters the growth of plants from seeds, is known to increase the total phenolic content of sunflower seeds by up to 232%.
This phenomenon holds significant implications for human health, as phenolic compounds have been demonstrated to possess antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that can aid in mitigating the risk of chronic diseases as part of a dietary routine.
- When sprouts reach a length of approximately one inch, they are considered suitable for consumption.
Selecting The Sunflower Seed
Organic produce is widely considered to be a better dietary choice than conventional food sources due to several key reasons;
- Firstly, organic food essential nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants may differ from conventional produce. This is because organic farmers use natural methods to fertilise and nourish the soil, which in turn helps to produce healthier and more nutrient-dense crops.
- Secondly, organic food is free from harmful pesticides, herbicides, and other chemicals that are commonly used in conventional farming practices. These chemicals can have a negative impact on the body, causing everything from skin irritation to more serious issues such as carcinogenic factors.
- Thirdly, organic food contains less preservatives or other additives that are used to extend the shelf life of mass-produced food products.
Ayurvedic Overview Of Sunflower Seeds
Sunflower seeds and oil are believed to have a balancing effect on Vata and Pitta as per Ayurvedic sciences. However, they may increase the Kapha qualities when consumed as seed.
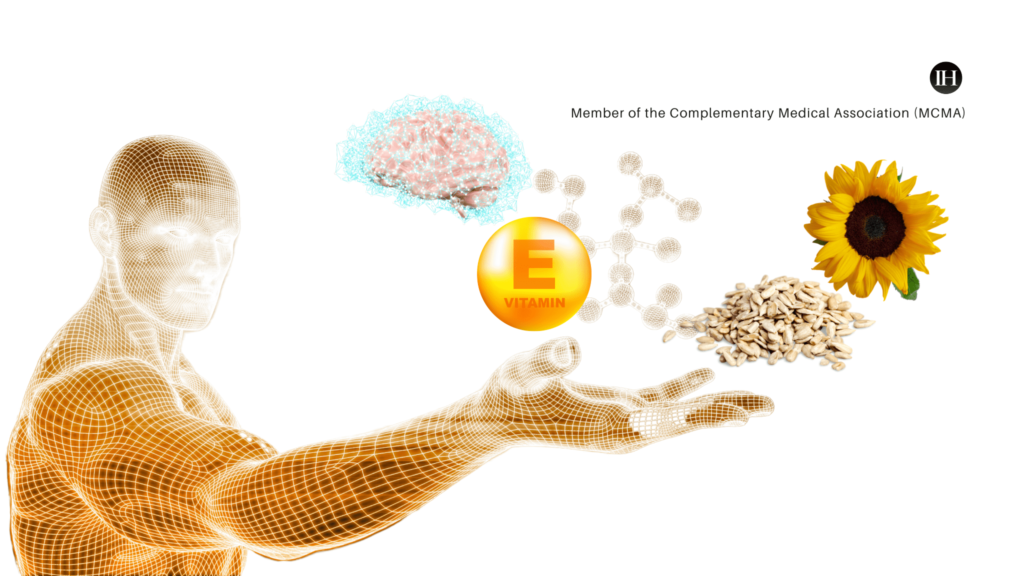
Ayurveda recognises sunflower seeds as good to eat for cognitive vitality due to their rich antioxidative compounds.
- Adding sunflower seeds to a well-balanced therapeutic diet can enhance one’s emotional well-being, thanks to the presence of linoleic and linolenic acids (omega 6 and 3) and other fatty acids.
- Moreover, seeds are rich in vitamin E, which has been shown to boost cognitive performance during the aging process and is considered an anti-aging agent.
However, the seed quality, oil and extraction methods are given considerable importance in relation to the preservation of constituents and their influence as a dietary therapeutic.

Summary
Sunflower seeds can be rich source of body-friendly nutrients in a diet and can offer many health & well-being benefits.
They are rich in nutrients and have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antidiabetic properties.
One of the best ways to consume them is by adding them to soups, salads, stews, or as a snack. They can also be germinated and consumed.
Several studies recognise the exceptional micro nutrients profile of these seeds, including chlorogenic acids, amino acids, quercetin, kaempferol, luteolin, apigenin and several others.
When consumed as part of a well-balanced diet, the seed compounds are associated with anti-obesity, anti-diabetic, and exceptional antioxidative actions, as recognised by several reputable studies.
Sunflower seeds are an easy to add source of nutrients.
Suitability & Precautions
Precautions and personal responsibility are crucial. Check the suitability of any diet, therapeutic or well-being routine, if pregnant, individuals with chronic health concerns and allergies. To make an informed choice, seek the advice of a professional.
This post is for informational purposes only and does not constitute professional advice.
References in this article
Petraru A, Ursachi F, Amariei S. Nutritional Characteristics Assessment of Sunflower Seeds, Oil and Cake. Perspective of Using Sunflower Oilcakes as a Functional Ingredient. Plants (Basel). 2021 Nov 17;10(11):2487. doi: 10.3390/plants10112487. PMID: 34834848; PMCID: PMC8619027.
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170562/nutrients
https://www.britannica.com/plant/sunflower-plant
La Fata G, Weber P, Mohajeri MH. Effects of vitamin E on cognitive performance during ageing and in Alzheimer’s disease. Nutrients. 2014 Nov 28;6(12):5453-72. doi: 10.3390/nu6125453. PMID: 25460513; PMCID: PMC4276978.
Guo S, Ge Y, Na Jom K. A review of phytochemistry, metabolite changes, and medicinal uses of the common sunflower seed and sprouts (Helianthus annuus L.). Chem Cent J. 2017 Sep 29;11(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s13065-017-0328-7. PMID: 29086881; PMCID: PMC5622016.
Leverrier A, Daguet D, Calame W, Dhoye P, Kodimule SP. Helianthus annuus Seed Extract Affects Weight and Body Composition of Healthy Obese Adults during 12 Weeks of Consumption: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Pilot Study. Nutrients. 2019 May 15;11(5):1080. doi: 10.3390/nu11051080. PMID: 31096648; PMCID: PMC6566515.
Easy Ayurveda: Top foods to promote mental health: https://www.easyayurveda.com/2011/05/26/top-foods-to-promote-mental-health/
Akkaya MR. Prediction of fatty acid composition of sunflower seeds by near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy. J Food Sci Technol. 2018 Jun;55(6):2318-2325. doi: 10.1007/s13197-018-3150-x. Epub 2018 Apr 19. PMID: 29892132; PMCID: PMC5976617.










